incastle의 콩나물
[경제성공학] Chapter 4. Nominal and Effective interest Rates 본문
경제성공학 김장호 교수님 수업 (19-1)
interst Rates
- 기존에 이자율은 년 단위로 update가 됐다.(ex. 1년이 지나면 이자가 얼마 오른다.)
- 현실 세계에서는 그 기간이 더 짧다. (반년마다, 분기마다, 월마다 등)
- even in our personal lives, many of our financial considerations have interest rates compounded shorter than once a year.
- nominal interest rate(명목 금리, 명목 이자율) vs effective interest rate(실효 금리, 실효 이자율)
- 검색해보면 [실질 금리 = 명목 금리 - 물가 상승률]이라는 말만 내놓는데 딱히 관련은 없어 보인다.
- compounded period가 변하면 nominal과 effective를 고려해야 한다.
Nominal interest rates
- interest rate that does not account for compounding
- r = interest rate per time period x number of periods (여기서 period = compounding period이다. compound가 어떤 주기로 반복되고, 몇 년도 안 이를 볼 거냐?)

- 위의 문제는 interest rate가 1.5%이고 한 달을 주기로 이자가 붙는다.
- time period = number of period와 동일. 한 달이라는 기간이 time period에 몇 번이나 들어가 있냐?라는 것
- 그것이 nominal interest rate
- 위의 표는 compounded period(CP)가 적혀 있지 않다. 은행에서는 이를 표현해줘야 한다. 가령 두 번째 time period(12 months 같은 경우) 18% per 1 year compounded monthly라고 하면 된다.
- 사실 chapter 1의 simple rate를 계산하는 방법과 동일하다.
- Nominal interest rate does not present the effect of compounding
Effective interest rate
- An effective interest rate i is a rate wherein the compounding of interest is taken into account.
>> 복리가 고려된 비율 = effective interest rate - effective interest rate는 compounding of interest 개념이 존재한다.
- CP가 안 적혀 있으면, it is the same as the period written in the interest rate
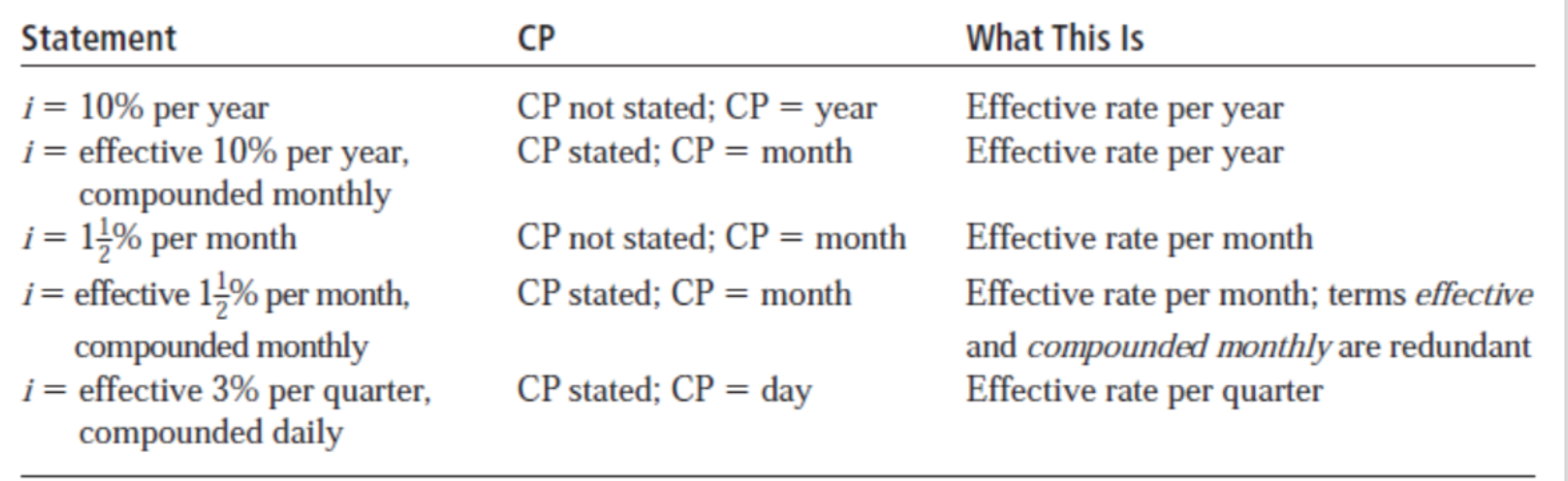
- 첫 번째 행 => CP가 안적혀 있다 => nominal interest rate와 period가 동일
- 두 번째 행 => compounded monthly => CP=month
interest Rates (2)
- 모든 nominal interest rate는 effective rate로 바꿀 수 있다.
- nominal rate는 r로, effective rate는 i로 표기한다.
- interest rate의 3요소
- interest period(t) : 이자가 붙는 기준 기간(주기)
- compounding period(CP) : compounding 주기가 어떠하니?(기준 기간과 compounding 되는 기간은 다름)
- compounding frequency(m) : t기간 동안 몇 번이나 compounding?
- 8% per year compounded monthly
- t = 1 year
- CP = 1 month
- m = 12
- 이자는 1년 동안 붙고, compounding은 한 달을 주기로 붙고 따라서 compounding은 12번 된다.
Effective rate per CP

- 분자로 들어가는 r을 다르게 표현하면 nominal rate. 즉 nominal rate를 m으로 나눈 것.
- example) 9% per year compounded monthly => effective rate per 1 month = 9%/12 = 0.75%
- interest period에 cp가 몇 번이나 들어가는지 check => 그 값이 m => nominal rate/m을 해준다.
Annual Percentage Rate(APR)
- APR is often stated as an annual rate for savings account, credit cards, loads, etc.
- ARR is the same as nominal rates
- example) APR of 15% can mean
- a nominal 15% per year
- a nominal 1.25% per year compounded monthly (nominal을 위에서 계산했듯이 1.25*12=15)
Effective annual interest rate
- effective interest rate는 annual rate(위에서는 annual percentate rate)라고도 함
- 계산 방법은 APR과 당연히 다르다.

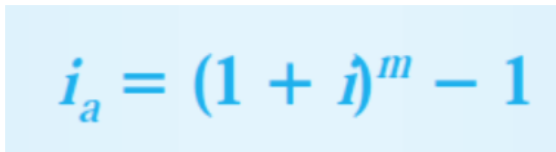
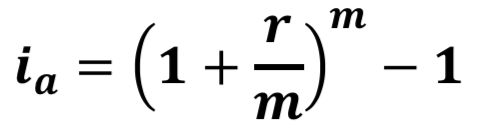
- This equation calculates the effective annual interest rate i_a for any number of compounding periods per year when i is the rate for on compounding period.
- 여기서 중요하다고 생각되는 건 t=1 year이라는 것. (annual이니까!!) 즉 r% per year이다.per year이 위배되면 사용 못함(혹은 변형해야 함)
- 문제에서 effective rate라고 명시돼서 주어졌는지, 그냥 interest rate라고 주어졌는지를 잘 확인해라.
Effective Interest Rates for Any Time Period
- 기존 Effective annual interest rate => 1년 단위였음
- r% per year => r/특정 값 per 특정 값으로 하면 annual이 아니라 얼마든지 바꿀 수 있음
Compound and Payment Periods
- Compounding period(CP) shows how often compounding takes effect
- Payment period(PP) is the length of time between cash flows
- CP < PP
- Find the effective rate i per PP
- Determine n as the total number of PP
# NOTE
1. It is common that the lengths of the payment period and the compounding period(CP) do not coincide.
=> PP랑 CP가 같지 않는 게 일반적임
2. (PP < CP)
>> If a person deposits money each month into a savings account where interest is compounded quarterly, do all monthly deposits earn interest before the next quarterly compounding time? => NO
>> If a person's credit card payment is due with interest on the 15th of the month, and if the full payment is made on the 1st, does the financial institution reduce the interest owed, bsed on early payment? => NO
# CP < PP
>> 현재 이자를 pp기준으로 맞춰준다.
3. For a no-interperiod-interest policy, negative cash flows(deposits or payments) are all regarded as made at the end of the compounding period, and positive cash flows(receipts or withdrawls) are all regarded as made at the beginning.
'19-1 대학 수업 > 경제성공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [경제성공학] Chapter 5. Present Worth Analysis -2- (0) | 2019.04.20 |
|---|---|
| [경제성공학] Chapter 5. Present Worth Analysis (0) | 2019.04.19 |
| [경제성공학] Chapter 3. Combining Factors and Spreadsheet Functions (0) | 2019.04.08 |
| [경제성공학] Chapter 2. Factors: How time and interest affect money (0) | 2019.04.08 |
| [경제성공학] Chapter 1. Foundations of Engineering Economy (0) | 2019.04.08 |