incastle의 콩나물
[경제성공학] Chapter 9. Benefit/Cost Analysis and Public Sector Econmics 본문
[경제성공학] Chapter 9. Benefit/Cost Analysis and Public Sector Econmics
incastle 2019. 6. 16. 00:16경제성공학 김장호 교수님 수업 (19-1)
Public Sector
- 공공부문과 service sector는 어떻게 경제성 분석을 할까?
- public project의 수혜자는 시민, residents of a government unit
Benefit/Cost Ratio
- benefit/cost ratio(이익 / 비용 (B / C) 비율)은 공공 부문 평가의 경제 분석에 객관성을 도입합니다.
>> 정치와 특수 이익의 영향을 줄인다.
- B/C 분석은 결과적으로는 PW, AW 및 ROR 분석과 동일한 대안을 선택합니다.
* benefit/cost ratio : 편익 비용 비율
9.1 Public Sector Projects
Public Sector

- 소유권(ownership) : 시민
- no profit으로 제공!
Public vs Private Sector (1)
- public은 초기 비용이 크고, 투자 기간도 길어

- profit은 없는데 benefit은 시민에게 간다.

- disbenefit도 존재함. public sector가 바람직하지 않은 결과를 발생시킬 수 있어.
- 경제 분석은 이러한 결과를 화폐 단위로 환산 해야해
B/C Analysis
- For B/C analysis, the costs, benefits, and disbenefits must be estimated, 가능한 정확하게!
- cost : 정부 기관에 대한 예상 지출
- benefits : public이 얻는 이득
- disbenefits : 대안이 실행될 때 public에게 끼칠 수 있는 직-간접적인 부정적 결과
- 그런데 사실 benefit, disbenefits 측정하는 건 어려움
Public vs Private Sector (2)
- public sector에서 투자할 돈은 국민들의 피 같은 세금!
- public sector에서 i는 굉장히 낮음.
- 공공 부문 평가를 위한 이자율 결정은 민간 부문 분석을 위한 MARR 결정만큼 중요합니다.
- 이때의 i를 discount rate라고 한다.
9.2 Benefit/Cost Analysis of a single Project
B/C ratio
- 모든 cost, benefit는 pw, aw, fw 등으로 변환됨(at the discount rate)
- then B/C는 계산됨

- cost는 양수임
- salvage value와 추가 revenue는 cost에서 뺀다. (cost - salvage value - revenue)
- B/C가 1보다 크면 project를 accept, discount rate applied
- B/C가 1보다 작으면 project ㄴㄴ
- B/C가 1이면, 비경제적 factor들이 의사결정에 도움을 줄 것임
Conventional B/C ratio

- disbenefit를 cost로 생각할 수도 있음, 하지만 일반적으로는 benefit에서 뺌.
- m&o는 분모에서 빼준다.
Modified B/C ratio

- 분모에는 initial investment만 적는다.
- conventional과 modified의 결과는 다름. 하지만 accept or reject에 대한 결과는 동일함
- m&o는 분자에서 빼준다.
9.3 Alternative Selection Using Incremental B/C Analysis
Incremental B/C Analysis ( 1 )
- 두 개의 mutually exclusive 대안을 B/C 분석으로 비교하는 것은 incremental ROR 분석과 동일하다
- incremental B/C ratio : 델타 B/C
>> PW, AW or FW 계산을 한다.
>> ΔB / C가 1보다 큰 경우, 더 높은 cost를 갖는 대안이 선택된다.
Incremental B/C Analysis ( 2 )
- 일단 각 대안의 B/C가 1보다 큰지 확인
- 큰 차이는 ordering of the alternatives이다.
>> lowest에서 highest total cost로 정렬
전체 Step
1) 각 대안의 equivalent total cost를 결정한다.
2) 작은 것에서 큰 순서로 정렬한다. larger-cost 대안에 대해 incremental cost를 계산한다. ΔB / C의 분모가 된다.
3) benefit, disbenefit 계산한다. larger-cost에 대해 incremental benefit를 계산한다.
4) ΔB / C를 계산한다.
5) 둘 다 ΔB / C가 1보다 크다면, higher-cost를 선택
*잘 안 와 닿음, 물어보기
Incremental B/C Analysis ( 3 )
- equal-life 비교를 요구함
- LCM or study period
- 대부분의 공공 부문 프로젝트의 useful-life는 길다는 것을 유의하십시오
9.5 Service Sector Projects and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Service sector projects ( 1 )
- service sector project는 개인, 비즈니스, 정부 기관에 제공하는 process 또는 system이다.
- 경제적 가치는 무형 자산임
ex) 헬스케어 시스템, 기차 예매 시스템 등
- 평가가 어려움
- 신호등을 설치하기
>> public이면서 service project임
>> economic benefit는 측정하기 어려움
- 화폐, 비화폐적 benefit를 평가하기 => cost-effectiveness analysis(CEA)
Service sector projects ( 2 )
- CEA는 cost-effectiveness ratio(CER)을 사용함
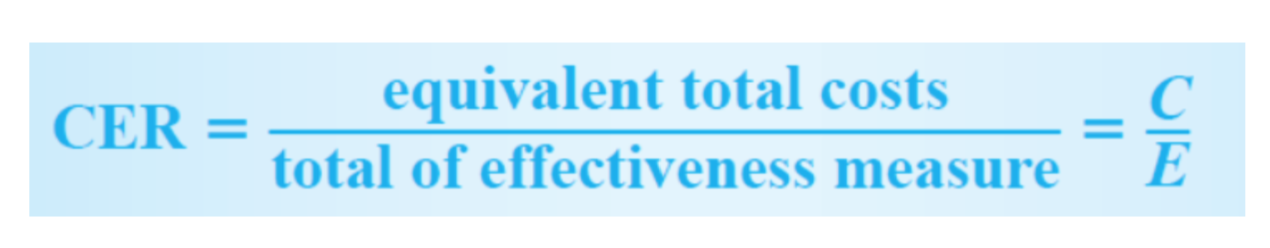
- 분자와 분모가 지금까지의 b/c ratio와 다르다
- 따라서 작은 CER(작다는 것은 cost가 작고 effectiveness는 큰 것이겠지)이 바람직하다.
- effectiveness로 정렬하고 incremental을 계산한다.
C/E Analysis
- independent project이면 허용된 예산 안쪽으로는 전부 선택
1) C, E, CER 모두 계산한다.
2) CER이 작은 것에서 큰 것 순으로 정렬
3) cumulative cost 계산, budget limit 괜찮나?
4) b 초과 안 하면 모두 선택
* incorporating a budget is called capital budgeting
* Selecting one among mutually exclusive alternatives requires incremental C/E analysis similar to ROR and B/C analyses.
상호 배타적인 대안 중 하나를 선택하려면 ROR 및 B / C 분석과 유사한 증분 C / E 분석이 필요합니다.
자세한 건 스킵한다!
'19-1 대학 수업 > 경제성공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [경제성공학] Chapter 12. Independent Projects with Budget Limitation (0) | 2019.06.15 |
|---|---|
| [경제성공학] Chapter 8. Rate of Return Analysis : Multiple Alternatives (0) | 2019.05.29 |
| [경제성공학] Chapter 7. Rate of Return Analysis : One Project (0) | 2019.05.27 |
| [경제성공학] Chapter 6. Annual Worth Analysis (0) | 2019.04.21 |
| [경제성공학] Chapter 5. Present Worth Analysis -2- (0) | 2019.04.20 |




