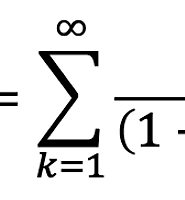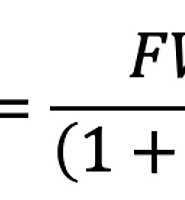incastle의 콩나물
Chapter2. The Basic Theory of Interest || Part1 본문
2.1 Principal and Interest
Principal : Amount invested (original amount)
Interest : Extra money paid on principal
Simple interest
- Interest will be paid only on the principal
- Account grows linearly with time
- V = A(1+r*n)
- V = Future value, A = 원금, r = 이자, n = 몇 년?

Compound interest
- Interest will be paid on the principal and accrued interest

- Rule of 72
- Money invested at R% compounded annually doubles in about 72/R years
- 돈이 2배가 되기 위해서는, R% 연복리일 때, 72/R년이면 2배가 된다.
Effective interest rate(실효 금리, 실제로 1년동안 복리를 계산했을 때 얼마냐? compound rate와 단위 통일 느낌)
- Equivalent yearly interest rate that would produce the same result after one year without compounding
- 복리없이 1 년 후 동일한 결과를 생성하는 동등한 연간 이자율
- example
- Annual rate of 8% compounded quarterly will produce an increase of
- Effective interest rate is 8.24% and nominal rate is 8%

Continuous Compounding
- m이 무한대로 간다면?

Discounting
- present value를 계산하기 위해서 미래의 가치를 가지고 와~
- (1+r)로 나눠 // compounding은 (1+r)로 곱하고
Discount Factor
-
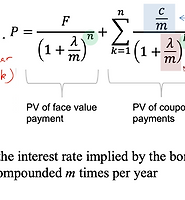
Present value of a future monetary amount is less than the face value of that amount

- Discount factor: Factor by which the future value must be discounted


'20-1 대학 수업 > 금융공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter4. Term Structure of Interest Rate || Part.1 (0) | 2020.04.17 |
|---|---|
| Chapter3. Fixed-Income Securities || Part2 (0) | 2020.04.16 |
| Chapter3. Fixed-Income Securities || Part1 (0) | 2020.04.14 |
| Chapter2. The Basic Theory of Interest || Part2 (0) | 2020.04.13 |
| Chapter1. Introduction (0) | 2020.04.12 |