incastle의 콩나물
Chapter2. The Basic Theory of Interest || Part2 본문
2.3 Present and Future Values of Streams
Future Value
-
This formula for future value always uses the interest rate per period and assumes that interest rates are compounded each period
Present Value
-
Present value of a cash flow is the present payment amount that is equivalent to the entire stream
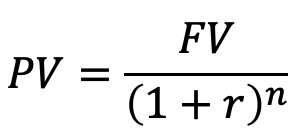
2.4 Internal Rate of Return
IRR
-
IRR is defined without reference to a prevailing interest rate
-
Determined entirely by the cash flows of the stream
-
Higher internal rate of return means the rate of return from investing V0 is high
- For any cash flow stream, the IRR is the interest rate that makes the present value of the stream to be zero
2.5 Evaluation Criteria
Evaluation with Net Present Value
-
Alternatives with higher present values are more desirable
-
All cash flows associated with the investment must be included (both positive and negative)
-
Net present value (NPV): Present value of benefits minus the present value of costs
-
Only investments with positive NPV are worthy of consideration
Evaluation with Internal Rate of Return
-
Alternatives with higher IRR are more desirable
-
Investment is not worth considering unless its IRR is greater than the prevailing interest rate
(IRR이 이자율보다 높지 않으면 투자 가치가 없습니다, 여기서는 비슷한 위험도라는 가정하에!)
NPV vs IRR
-
NPV: simplest to compute; can be broken into component pieces
-
IRR: depends only on the properties of the cash flow stream; does not require external interest rate
-
For one-time investments, NPV may be more appropriate
-
If future cash flows from reinvestment were modeled, NPV may provide the same recommendation as IRR
-
One approach is to use NPV as the first evaluation criterion and check IRR to confirm the result
-
NPV and IRR are good starting points but other factors also need to be considered
'20-1 대학 수업 > 금융공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter4. Term Structure of Interest Rate || Part.1 (0) | 2020.04.17 |
|---|---|
| Chapter3. Fixed-Income Securities || Part2 (0) | 2020.04.16 |
| Chapter3. Fixed-Income Securities || Part1 (0) | 2020.04.14 |
| Chapter2. The Basic Theory of Interest || Part1 (0) | 2020.04.12 |
| Chapter1. Introduction (0) | 2020.04.12 |



