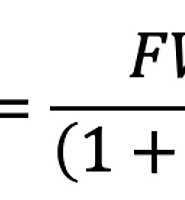incastle의 콩나물
Chapter3. Fixed-Income Securities || Part1 본문
Definitions
-
Financial instruments : Market items are not real goods (no intrinsic value, 무형 자산) but instead are traded as only as pieces of paper or as entities in a computer database
-
Security(증권): Instrument that can be freely and easily traded due to a well- developed market for the instrument
- Fixed-income securities : Financial instruments that are traded in well- developed markets and promise a fixed income to the holder over a span of time
- Fixed-income securities are important because they define the market for money
3.1 The Market for Future Cash
Fixed-income securities
-
Only uncertainty is whether the issuer of the security might default
유일한 불확실성은 발행자가 채무 불이행을 할 때임 -
Some fixed-income securities promise cash flows tied to various contingencies or fluctuating indices
일부 fixed-income securities는 다양한 우발 상황 또는 변동 지수와 관련된 현금 흐름을 약속함
Savings Deposits(저축 예금 계좌)
-
Bank deposit is probably the most familiar fixed-income instrument
Mortgages
-
Mortgage looks like the opposite of a bond
-
Future homeowner sells a home mortgage to generate immediate cash to pay for a home and is obligated to make periodic payments to the mortgage holder
미래 주택 소유자는 주택 담보 대출을 판매하여 주택에 지불 할 현금을 즉시 창출하며 주택 담보 대출 소유자에게 정기적으로 지불해야합니다 -
Standard mortgage is structured so that equal monthly payments are made throughout its term (in contrast to bonds that pay face value at maturity)
Annuities(연금)
-
Annuity: Contract that pays the holder (annuitant) money periodically according to a predetermined schedule or formula over a period of time
일정 기간 동안 미리 정해진 일정이나 공식에 따라 보유자에게 정기적으로 지불하는 계약 -
Annuities are not securities since they are not traded, but are considered to be investment opportunities (serve the same role as other fixed-income securities)
3.2 Value Formulas
Perpetual annuity(perpetuity)


Finite-Life Streams
- 영원히 반복되는 게 아니라, 끝이 있다면?

-
Note that r is expressed as a per-period interest rate
-
Annuity formula is also used in the reverse direction => Determines the periodic payment that is equivalent to an initial payment of P
-
Amortization(할부 상환): Process of substituting periodic payments for a current obligation (e.g. amortize the cost of an automobile over 5 years by taking out a 5-year loan)
할부 상환 : 현재의 채무를 정기적으로 대체하는 절차 (예 : 5 년 동안 대출을 받아 5 년 이상 자동차 비용을 상각)

3.3 Bond Details
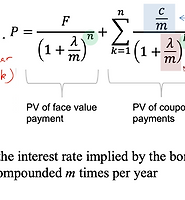
Bond
-
Obligation by the bond issuer to pay money to the bond holder according to rates specified
지정된 요율에 따라 채권 발행인이 채권 보유자에게 돈을 지불 할 의무 -
Bonds represent the greatest monetary value of fixed-income securities and are the most liquid of these securities
채권은 고정 수입 증권의 가장 큰 금전적 가치를 나타내며 이러한 증권 중 가장 유동적입니다 -
Most bonds pay periodic coupon payments
- Most bonds are sold either at auction or through an exchangeèPrice is determined by a market and thus may vary constantly
Bond Coupons
-
Last coupon date corresponds to the maturity date, so that last payment is equal to the face value plus the coupon value
-
Coupon amount is described as a percentage of the face value
Example: 9% coupon bond with a face value of $1,000 will have a coupon of $90 per year
Quality Ratings
-
Bonds with low rating will have a lower price May be good investment opportunity if the default risk can be diversified


'20-1 대학 수업 > 금융공학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Chapter4. Term Structure of Interest Rate || Part.1 (0) | 2020.04.17 |
|---|---|
| Chapter3. Fixed-Income Securities || Part2 (0) | 2020.04.16 |
| Chapter2. The Basic Theory of Interest || Part2 (0) | 2020.04.13 |
| Chapter2. The Basic Theory of Interest || Part1 (0) | 2020.04.12 |
| Chapter1. Introduction (0) | 2020.04.12 |