incastle의 콩나물
[SCM] Chapter 11. Managing Economies of Scale in a Supply Chain : Cycle Inventory || Part2 본문
[SCM] Chapter 11. Managing Economies of Scale in a Supply Chain : Cycle Inventory || Part2
incastle 2020. 6. 9. 00:3611.3 Aggregating Multiple Products in a Single order : 여러 제품을 단일 주문으로 통합하는 경우
로트당 고정비를 낮추는 건 중요, 그중에서도 수송비!
기업은 group을 나눠서 재고 관리 => group을 적절히 결합하자.
- Aggregating replenishment across products in a single order allows for a reduction in lot size for individual products, because transportation and other fixed ordering costs are spread across multiple products.
- 운송 및 기타 고정 주문 비용이 여러 제품에 분산되므로 단일 주문으로 제품 간 보충을 집계하면 개별 제품의 로트 크기를 줄일 수 있습니다.
- Other ways to achieve aggregation include having a single delivery coming from multiple suppliers or having a single delivery to multiple retailers.
- 집계를 달성하기위한 다른 방법으로는 여러 공급 업체로부터 단일 배송을 받거나 여러 소매 업체에 단일 배송을하는 것이 있습니다.
- 그러니까 소매점이 여러 공급자에게 주문을 하지만, 배송은 단일로 하는 거지 혹은 여러 소매점이 공동 구매를 하는 것도 방법이고
- As more product are included in a single order when attempting to reduce lot sizes, try to reduce the receiving and storing costs which are fixed costs.
- 로트 크기를 줄이려고 할 때 더 많은 제품이 단일 주문으로 포함되므로 고정 비용인 입고 및(receiving) 보관 비용을(storing cost) 줄이십시오.
Lot Sizing with Multiple Products
고정 비용
1) Common or joint order cost(공통 주문비) : 제품 다양성과 무관하게 발생
ex) 수송 비용
2) Product - specific order cost(제품 고유 주문비) : 제품 다양성에 의존하여 발생
ex) loading cost, receiving cost, storing cost
- 위의 방식을 적절하게 조합해서 3가지로 나뉨
-
Lots are ordered and delivered independently for each product model
-
Lots are ordered and delivered jointly for all models
-
Lots are ordered and delivered jointly for a selected subset of models
Lessons from Aggregation
- Aggregation across products, customers (retailers), or suppliers allows firms to lower lot size (or cycle inventory) without increasing cost
- 제품, 고객 (소매 업체) 또는 공급 업체에 대한 집계를 통해 회사는 비용을 증가시키지 않고 로트 크기를(혹은 cycle inventory) 줄일 수 있다.
- Complete aggregation is effective if product-specific fixed cost is a small fraction of common fixed cost and demand difference among products are not significant
- 제품 별 고정 비용이 일반 고정 비용의 작은 비율이며 제품 간 수요 차이가 크지 않은 경우 전체 집계(complete aggregation)가 효과적입니다
- Tailored aggregation is effective if product-specific fixed cost is a large fraction of common fixed cost and demand difference among products are significant
- 제품 별 고정 비용이 일반 고정 비용의 큰 부분이며 제품 간 수요 차이가 큰 경우 맞춤형 집계(tailored aggregation)가 효과적입니다.
11.4 Economies of Scale to Exploit Quantity Discounts : 수량 할인을 이용한 규모의 경제
Quantity discount
- Lot size-based quantity discount : 주문량 기준 할인(한번에 주문하는 양 기준으로)
- all unit quantity discount : 총단위 수량 할인
- marginal unit quantity discount : 증분단위 수량 할인
- volumne-based quantity discount : 수량 기준 할인(총량을 기초로)
Two basic questions
구매자의 입장에서 어떻게 구매하는 게 가장 최적인가?
판매자의 입장에서 어떤 할인 정책을 재공해야 최적인가?
Quantity discounts 는 공급사슬 전체의 이익을 올릴 수 있기 때문에(협력을 통해서) 중요함
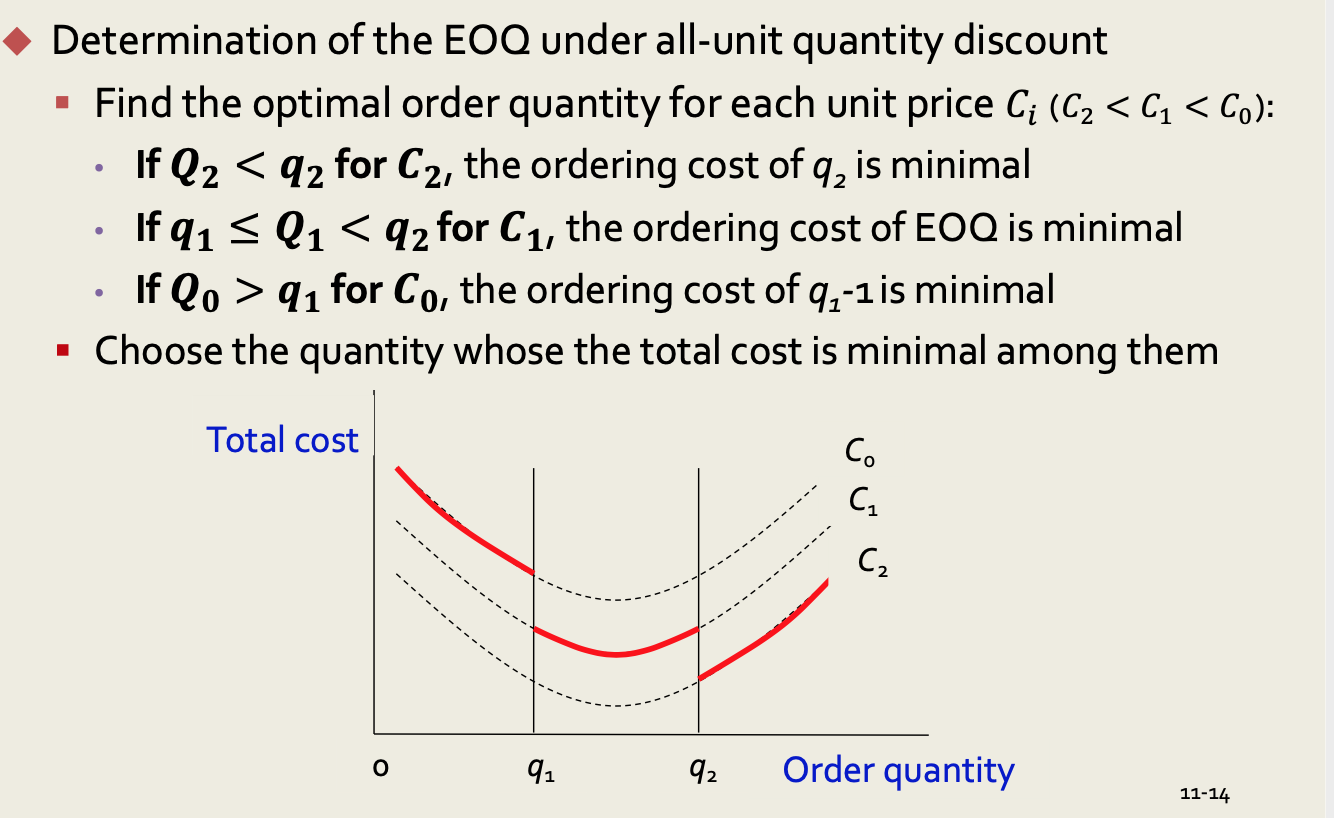
All-Unit Quantity Discounts : 총 단위 수량 할인

- 구매량에(q) 따라서 이미 평균 가격이 정해져있음
- q_i+1과 q_i 사이에 구매량이 있으면 C_i 로 구매하게 됨!
- 당연히 q1+1 단위로 구매하는 것이 q1-1 단위로 구매하는 것 보다 단가가 더 저렴해짐
Marginal Unit Quantity Discount(증분 단위 수량 할인 or 한계 단위 수량 할인)
- 구매량이 있고 => 모든 구매량을 같은 단위로 할인하는 게 아니라 MAX양이 있음

11.5 Why Do Suppliers Offer Quantity Discounts
- 공급자와 소매점 사이의 협력을 통해서 공급자의 이익을 올리기 위해서는 몇 가지 시나리오가 있다
Case1 : For commodity products(일회용품에 대해서)\
- 제품 수명주기 단계로 보면 성숙기에 있는 제품이다.
- 따라서 시장은 경쟁적이고, 시장이 가격을 결정한다. Ex) 우유, 비타민
- 회사의 목적은 이익을 증가하기 위해서 비용을 낮추는 것이다.
Case2 : For products for which the firm has market power
- 소매점이 가격을 결정한다. 예를 들어서 새로운 제품, 수요는 가격에 의해서 영향을 받는다.
- 회사의 목적은 높은 수익을 얻는 것
'20-1 대학 수업 > SCM' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SCM] Chapter 11. Managing Economies of Scale in a Supply Chain : Cycle Inventory || Part1 (0) | 2020.06.06 |
|---|---|
| [SCM] Chapter 10. Coordination in a Supply Chain / 공급사슬에서의 판매 및 운영 계획 (0) | 2020.06.05 |
| [SCM] Chapter 9. 공급사슬에서의 판매 및 운영 계획 (0) | 2020.06.03 |
| [SCM] Chapter8-1 Aggregate Planning in a Supply Chain (0) | 2020.06.02 |
| [SCM] Network Desigin in the Supply Chain,공급사슬에서의 네트워크 설계 (0) | 2020.04.23 |



