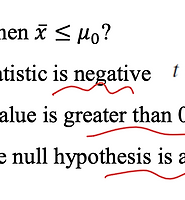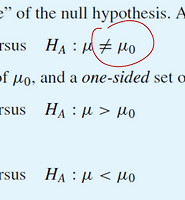incastle의 콩나물
[응용통계학] Chapter 8-2. Inferences on a Population Mean 본문
Effect of Sample Size
- sample size n은 confidence interval length에 영향을 미친다.

- 큰 sample size를 가지면, 작은 confidence interval을 가진다.
- 그런데 critical point(t)도 n에 영향을 받는데, 그 영향은 미미하기 때문에 L과 n사이의 관계를 표현할 때는 무시한다.
- 특정 길이의 신뢰 구간을 얻기 위해 필요한 표본 크기 n을 결정할 수도 있음
- 만약에 L_0보다 작은 confidence interval(Length)을 갖고 싶다고 한다면 필요한 n 사이즈를 아래와 같이 조절 가능

- 좀 더 정확하게 표현하려면, critical point(t)에서 사용되는 n과 좌변의 n은 다른 값이므로

- 이렇게 표현 가능하다. (n_1은 initial sample size)
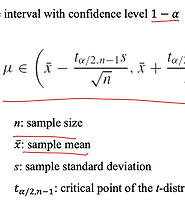
t-intervals
- 왜 t-interval formula는 make sense 한가?
- 유도 과정을 엄청 설명하는데... 알아야 하는지 모르겠음... 일단 skip
One-Sided t-intervals
- upper bound and lower bound




Z-intervals
- In some cases, one may wish to use the known value of the population standard deviation σ
어떠한 경우에는 알려진 모집단의 표준편차를 사용하고 싶을 수도 있음 - In this case, for a two-sided confidence interval, the standard normal critical point Z_𝛼/2 is used in place of t_𝛼/2,𝑛−1이 경우에 사용하는 two-siede confidence interval이 Z_𝛼/2다.

Z-interval vs t-interval
-
When a confidence interval for a population mean is required, t-interval should be almost always used
모집단 평균에 대한 신뢰 구간이 필요한 경우 거의 항상 t-interval을 사용해야 합니다. - 실험자가 모집단 표준 편차 σ에 대한 이전 실험의 사전 정보를 가지고 있고, 이 값을 사용하려는 경우 z- 간격이 적절할 수 있습니다.
- large sample size에서는 t와 z의 critical point 약간 다르다.
- z 구간을 큰 표본 신뢰 구간으로 생각하고 t 구간을 작은 표본 신뢰 구간으로 생각하면 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
'20-2 대학수업 > 응용통계학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [응용통계학] Chapter 9-1. Comparing Two Population Means (0) | 2020.10.10 |
|---|---|
| [응용통계학] Chapter 8-4. Inferences on a Population Mean (0) | 2020.10.09 |
| [응용통계학] Chapter 8-3. Inferences on a Population Mean (0) | 2020.10.08 |
| [응용통계학] Chapter 8-1. Inferences on a Population Mean (0) | 2020.09.30 |