incastle의 콩나물
[응용통계학] Chapter 9-1. Comparing Two Population Means 본문
Two Population Distribution

- sample size A, B는 서로 사이즈가 달라도 괜찮음
- 각각은 x_i, y_i는 각 집단에서 independent하게 뽑혔음
- In general, interested in assessing evidence that there is a difference between the two probability distributions
Two Population Means
- if we find the A의 평균 != B의 평균 => this indicates that the two probability distributions are different
- 만약에 A의 평균 = B의 평균임을 밝힌다면
- two probability distribution이 같다고 결론 내릴 수 있게 됨
- or we may further compare the variances of the two data sets
- How do we compare 𝜇_A and 𝜇_B?

- we want to see if the two are the same, we construct a confidence interval for 𝜇_A − 𝜇_B
- We are interested whether this confidence interval contains zero
- another approach => hypothesis test
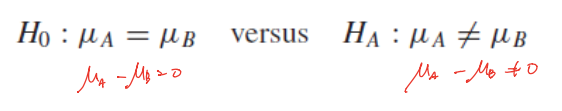
- small p-value => reject H0
Paired vs Independent sample
- 두 집단을 비교할 때는 paired할 수도 있고 independent 할 수도 있다.
- Paired samples may alleviate variability from outside factors
Paired
- sample size => must be equal
- Comparison between the two is then based upon the pairwise differences
그런 다음 둘 간의 비교는 쌍별 차이를 기반으로합니다.
Analysis of Paired Samples

- 이 z_i도 평균이 μ인 독립적인 하나의 분포로 해석할 수 있다. 그렇게 되면 one-sample technique을 적용할 수 있게 됨
- p-value로 검증을 하기 위해서 각 집단의 평균값을 사용함
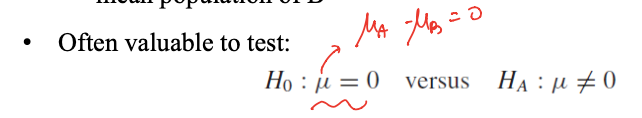
- each observation obtained from population A is thought of as below

- 이걸 A집단, B집단으로 나눠서 생각하고 그 둘의 차이를 구하면


- paired sample이기 때문에 r_i 두 개는 같아서 없어졌음
- 에러텀은 평균이 0인 분포를 가정했기 때문에 사라짐
Analysis of Independent(unpaired) Samples
- Independent samples
- x-y의 confidence level 을 측정할면 x-y의 standard error를 계산해야 함
- sample distribution의 standard error를 사용
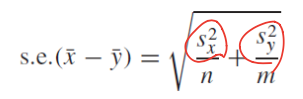

- critical point, s.e를 알아야함.


'20-2 대학수업 > 응용통계학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [응용통계학] Chapter 8-4. Inferences on a Population Mean (0) | 2020.10.09 |
|---|---|
| [응용통계학] Chapter 8-3. Inferences on a Population Mean (0) | 2020.10.08 |
| [응용통계학] Chapter 8-2. Inferences on a Population Mean (0) | 2020.10.05 |
| [응용통계학] Chapter 8-1. Inferences on a Population Mean (0) | 2020.09.30 |
Comments




